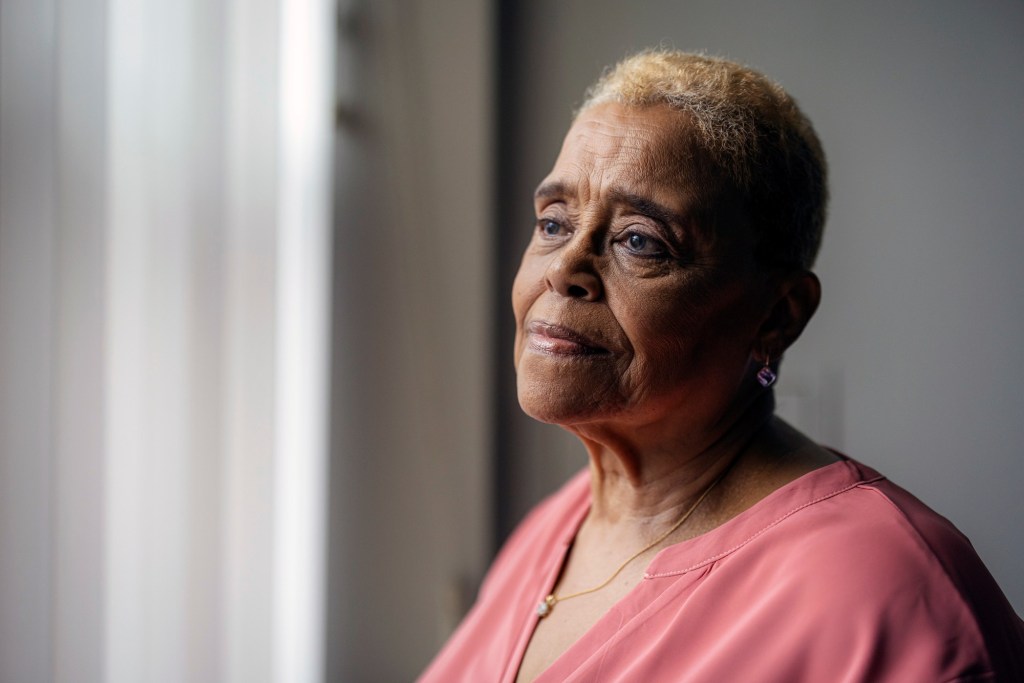
Gerri Norington, 78, never wanted to be on her own as she grew old.
But her first marriage ended in divorce, and her second husband died more than 30 years ago. When a five-year relationship came to a close in 2006, she found herself alone — a situation that has lasted since.
“I miss having a companion who I can talk to and ask ‘How was your day?’ or ‘What do you think of what’s going on in the world?’” said Norington, who lives in an apartment building for seniors on the South Side of Chicago. Although she has a loving daughter in the city, “I don’t want to be a burden to her,” she said.
Norington is part of a large but often overlooked group: the more than 16 million Americans living alone while growing old. Surprisingly little is known about their experiences.
This slice of the older population has significant health issues: Nearly 4 in 10 seniors living alone have vision or hearing loss, difficulty caring for themselves and living independently, problems with cognition, or other disabilities, according to a KFF analysis of 2022 census data.
If help at home isn’t available when needed — an altogether too common problem — being alone can magnify these difficulties and contribute to worsening health.
Studies find that seniors on their own are at higher risk of becoming isolated, depressed, and inactive, having accidents, and neglecting to care for themselves. As a result, they tend to be hospitalized more often and suffer earlier-than-expected deaths.
Getting medical services can be a problem, especially if older adults living alone reside in rural areas or don’t drive. Too often, experts observe, health care providers don’t ask about older adults’ living situations and are unaware of the challenges they face.
During the past six months, I’ve spoken to dozens of older adults who live alone either by choice or by circumstance — most commonly, a spouse’s death. Some have adult children or other…
Read the full article here