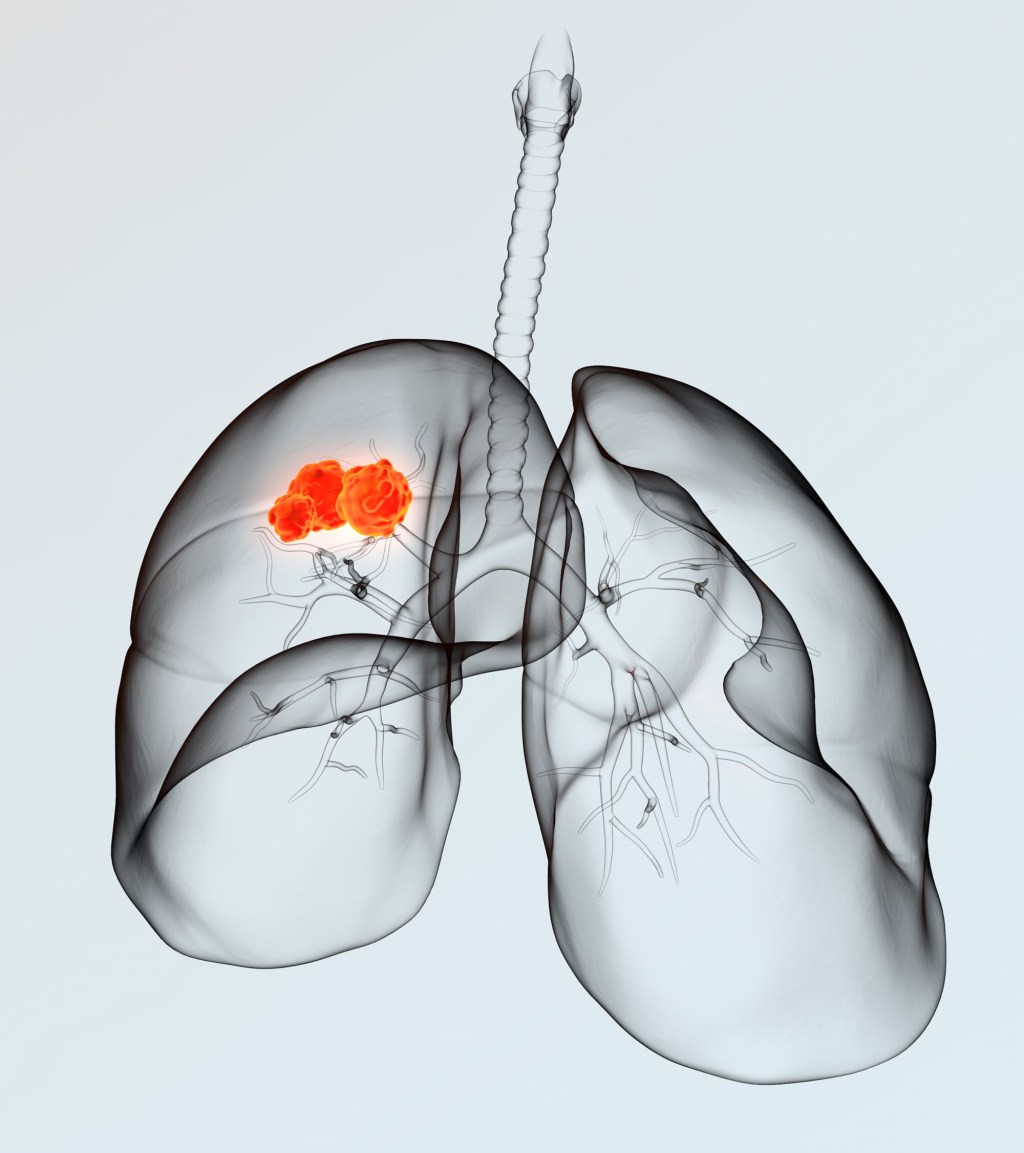
Lung cancer typically doesn’t cause signs and symptoms in its earliest stages. Signs and symptoms typically occur when the disease is advanced and may include:
— A new cough that doesn’t go away
— Coughing up blood, even a small amount
— Shortness of breath
— Chest pain
— Hoarseness
— Losing weight without trying
— Bone pain
— Headache
Risk factors
A number of factors may increase your risk of lung cancer. Some risk factors can be controlled, for instance, by quitting smoking. And other factors can’t be controlled, such as your family history.
Risk factors for lung cancer include:
— Smoking. Although the disease can occur in people who have never smoked, people who smoke or have smoked have the greatest risk of lung cancer. Your risk increases with the number of cigarettes you smoke each day and the number of years you have smoked. Quitting at any age can significantly lower your risk of developing lung cancer.
— Exposure to secondhand smoke. Even if you don’t smoke, your risk of lung cancer increases if you’re exposed to secondhand smoke.
— Previous radiation therapy. If you’ve undergone radiation therapy to the chest for another type of cancer, you may have an increased risk of developing lung cancer.
— Exposure to radon gas. Radon is produced by the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock and water that eventually becomes part of the air you breathe. Unsafe levels of radon can accumulate in any building, including homes.
— Exposure to asbestos and other carcinogens. Workplace…
Read the full article here