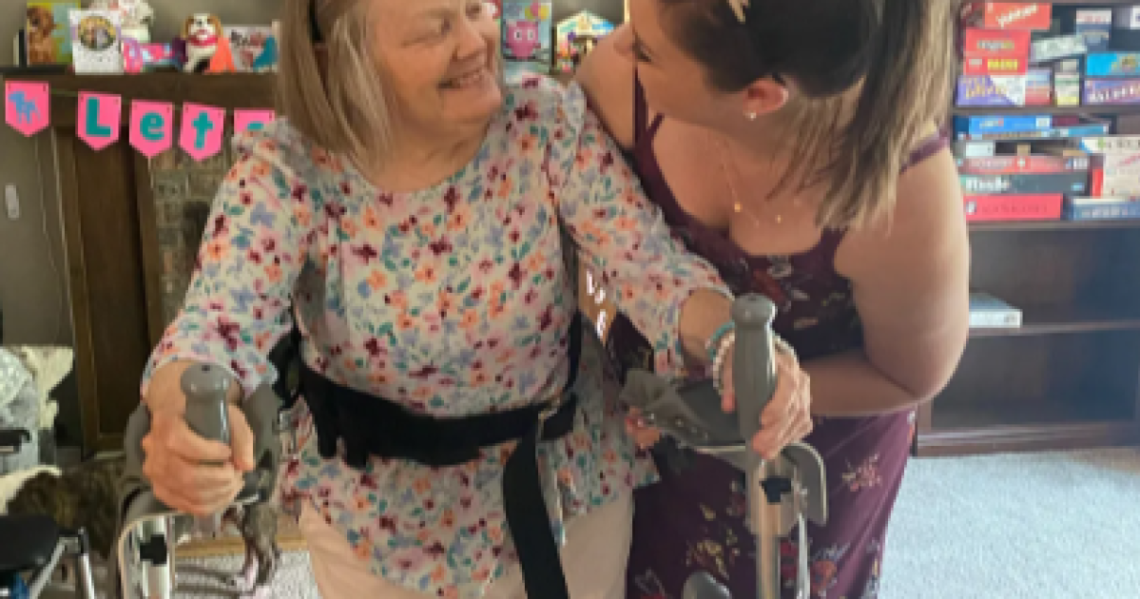
Even with extensive caregiving experience, Patti LaFleur was unprepared for the crisis that hit in April 2021, when her mother, Linda LaTurner, fell out of a chair and broke her hip.
LaTurner, 71, had been diagnosed with early-onset dementia seven years before. For two years, she’d been living with LaFleur, who managed insulin injections for her mother’s Type 1 diabetes, helped her shower and dress, dealt with her incontinence, and made sure she was eating well.
In the hospital after her mother’s hip replacement, LaFleur was told her mother would never walk again. When LaTurner came home, two emergency medical technicians brought her on a stretcher into the living room, put her on the bed LaFleur had set up, and wished LaFleur well.
That was the extent of help LaFleur received upon her mother’s discharge.
She didn’t know how to change her mother’s diapers or dress her since at that point LaTurner could barely move. She didn’t know how to turn her mother, who was spending all day in bed, to avoid bedsores. Even after an occupational therapist visited several days later, LaFleur continued to face caretaking tasks she wasn’t sure how to handle.
“It’s already extremely challenging to be a caregiver for someone living with dementia. The lack of training in how to care for my mother just made an impossible job even more impossible,” said LaFleur, who lives in Auburn, Washington, a Seattle suburb. Her mother passed away in March 2022.
A new proposal from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services addresses this often-lamented failure to support family, friends, and neighbors who care for frail, ill, and disabled older adults. For the first time, it would authorize Medicare payments to healthcare professionals to train informal caregivers who manage medications, assist loved ones with activities such as toileting and…
Read the full article here