This is part of a series of South Florida Sun Sentinel articles exploring maternal health care.
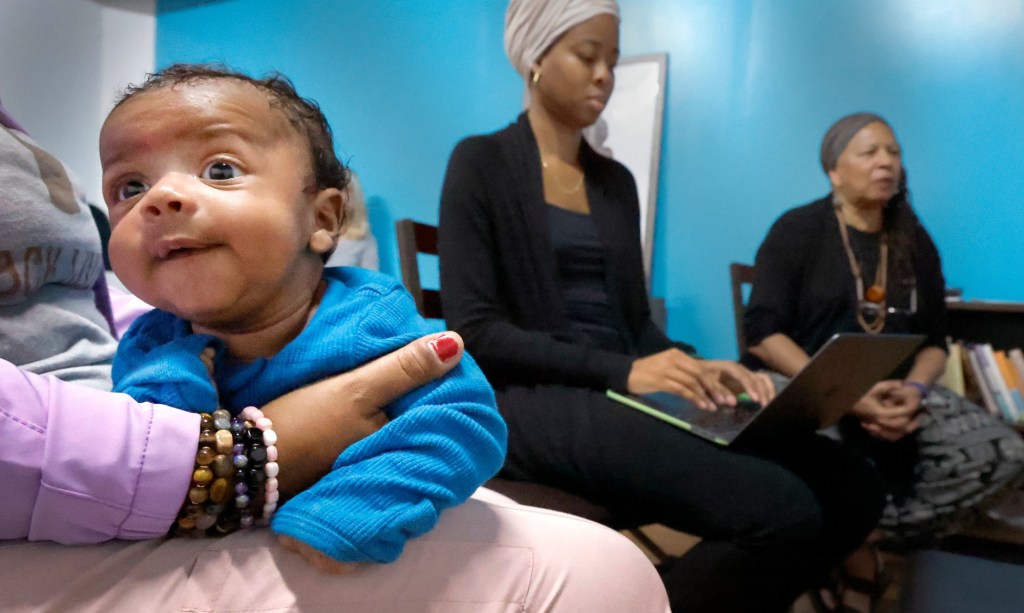
It is 2 a.m. when Brianca Spence slips behind the wheel of her car. The drive to the nearest hospital can stretch as long as an hour, and feel like an eternity when she’s rushing to guide an expecting mother through childbirth.
As labor unfolds, Spence will translate the harsh demands of a nurse on duty into calming guidance. She will encourage the woman to ask for pain medication when she needs it or suggest a position change to speed up labor. And, when the mother eventually returns home with a new baby, Spence will be her pillar of support, encouraging her to stick with breastfeeding, or go for her postpartum doctor’s visit.
Babies born early, ill, or dead: Florida spends millions on prevention. Why isn’t it getting better?
In this maternity care desert on the western fringes of Palm Beach County, Spence’s mission as a doula is to advocate for mother and baby before, during and after childbirth. If she does her job well, she will play a vital role in keeping more Black mothers and babies alive.
With Florida’s infant mortality rate stubbornly higher than the national average and Black babies in the state dying at more than double the rate of white non-Hispanic babies, doulas represent a potential pathway to address the problem.
Doula training has ramped up in the state, the result of a confluence of factors that are making the option more available to women — particularly women of color — who may benefit most from having an advocate through the process. Doulas are non-medical, trained labor assistants or coaches who provide physical and emotional support during pregnancy, childbirth and recovery. A doula will speak up for a mother when a doctor dismisses her concerns. She will ensure a woman’s birth plan is followed as much as possible. And, she will pick up on signs of complications or postpartum depression that could have been overlooked.
There’s no…
Read the full article here