It was an every-other-day routine, full of frustration.
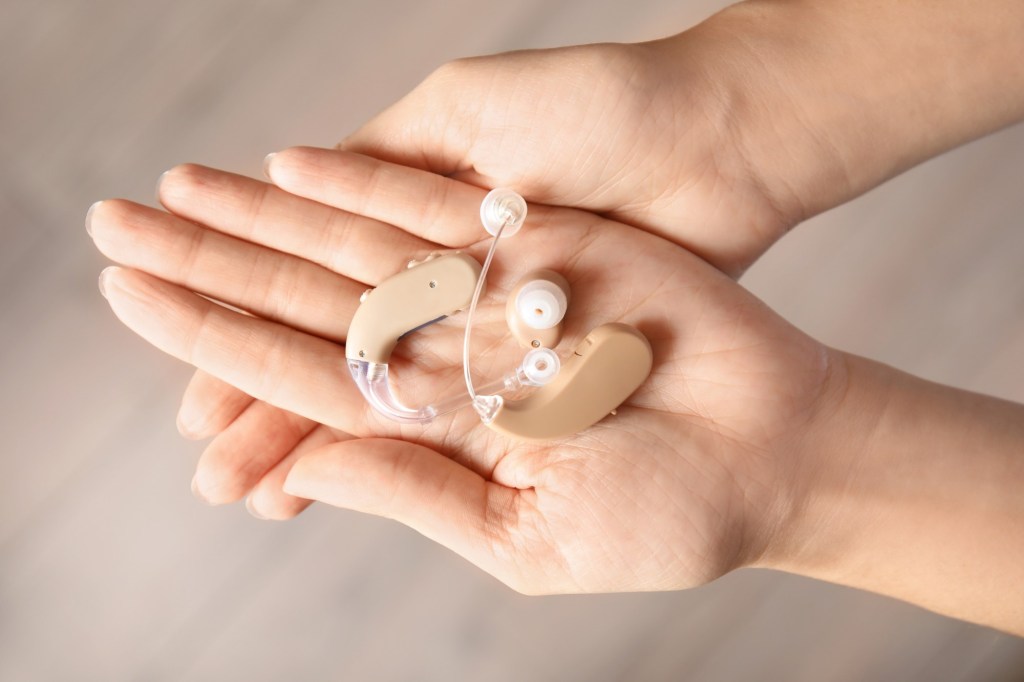
Every time my husband called his father, who was 94 when he died in 2022, he’d wait for his dad to find his hearing aids and put them in before they started talking.
Even then, my father-in-law could barely hear what my husband was saying. “What?” he’d ask over and over.
Then, there were the problems my father-in-law had replacing the devices’ batteries. And the times he’d end up in the hospital, unable to understand what people were saying because his hearing aids didn’t seem to be functioning. And the times he’d drop one of the devices and be unable to find it.
How many older adults have problems of this kind?
There’s no good data about this topic, according to Nicholas Reed, an assistant professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health who studies hearing loss. He did a literature search when I posed the question and came up empty.
Reed co-authored the most definitive study to date of hearing issues in older Americans, published in JAMA Open Network last year. Previous studies excluded people 80 and older. But data became available when a 2021 survey by the National Health and Aging Trends Study included hearing assessments conducted at people’s homes.
The results, based on a nationally representative sample of 2,803 people 71 and older, are eye-opening. Hearing problems become pervasive with advancing age, exceeding 90% in people 85 and older, compared with 53% of 71- to 74-year-olds. Also, hearing worsens over time, with more people experiencing moderate or severe deficits once they reach or exceed age 80, compared with people in their 70s.
However, only 29% of those with hearing loss used hearing aids. Multiple studies have documented barriers that inhibit use. Such devices, which Medicare doesn’t cover, are pricey, from nearly $1,000 for a good over-the-counter set (OTC hearing aids became available in…
Read the full article here