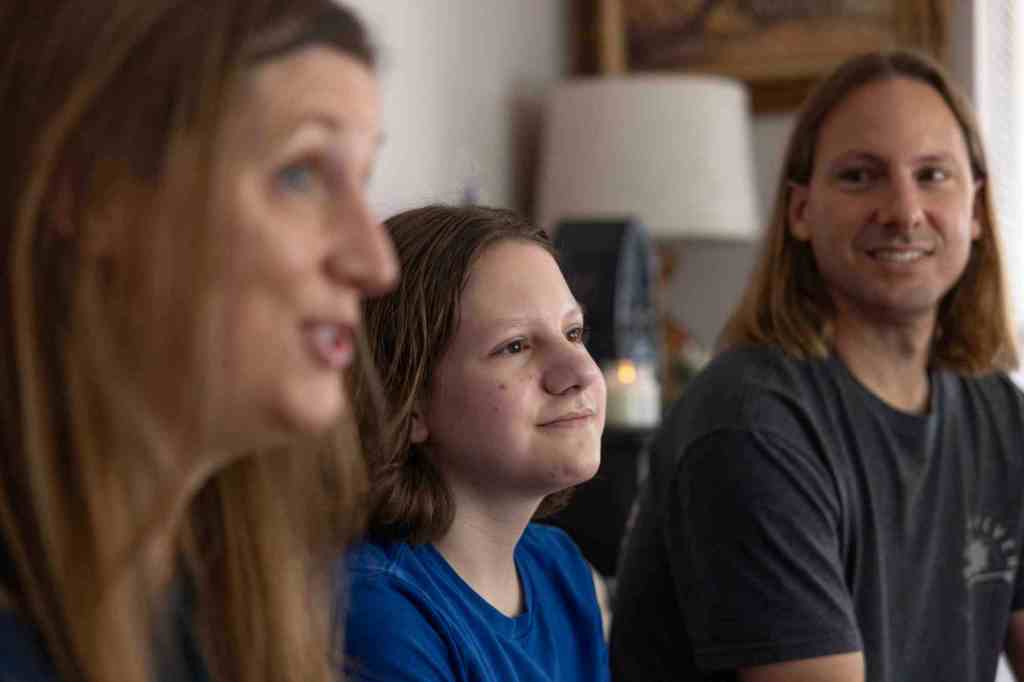Lauren J. Mapp | The San Diego Union-Tribune
When Vista resident Michelle Harvey packed an overnight bag so her son could undergo testing at Rady Children’s Hospital in June 2020, she expected to return home the following day. Instead, Mason Harvey was hospitalized for two months as he was diagnosed and subsequently treated for Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory bowel disease marked by chronic inflammation in the digestive system.
Prior to his hospital stay, a blood test showed that Mason had low levels of hemoglobin — the protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. He weighed about 45 pounds, much lower than the 60 to 120 pounds that is typical for an 11-year-old boy.
Mason was diagnosed nine days into his hospital stay, but before he could be sent home, doctors wanted to ensure he was in stable condition. For four weeks of his stay, he was on “gut rest,” meaning he was unable to eat solid foods.
“It was pretty hard because I like snacks and stuff, especially when going through hard times,” said Mason, who is now 14. “I was getting shots and things, but I couldn’t eat anything; I couldn’t even drink water.”
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that the National Institutes of Health estimates impacts half a million people throughout the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that 1.3 percent of American adults — about 3 million people — are diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease, meaning they have either a form of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Living with an inflammatory bowel disease can make many people feel alone, because they are reluctant to share their experience, said Iris Magid, executive director for the Greater San Diego & Desert Area Chapter of the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation.
“It’s really an isolating disease, and it’s a silent disease because you can’t tell if someone has Crohn’s or colitis just by looking at…
Read the full article here