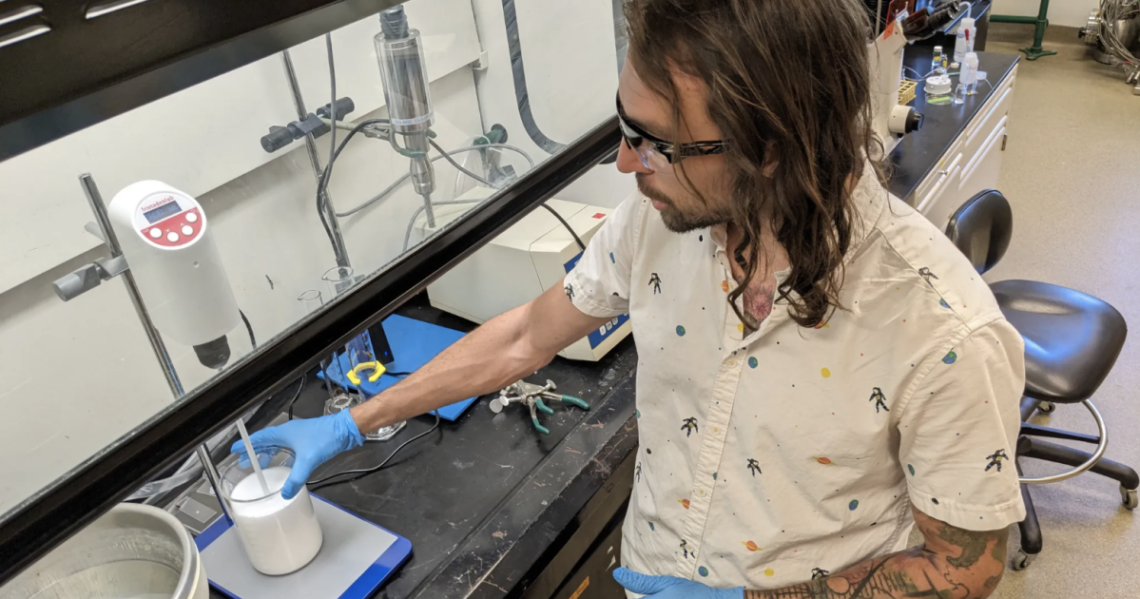
Mad-scientist kind of moments happen fairly often for nanoengineer Carson Bruns. A few months ago in his lab at the University of Colorado-Boulder, he tested his latest invention on his own arm and asked a colleague for help.
“We were like, ‘OK, we’re going to tattoo ourselves. Can you help us today?’” he said.
The tattoo is like a freckle, a little blue dot. But he can turn it on and off. Like the way a mood ring changes color with temperature, this tattoo changes with light: Ultraviolet light to turn it on, daylight (or even a flashlight) to turn it off.
“You can go to court and turn it off, and then go to the party and turn it on. And then go to Grandma’s house and turn it off,” said Bruns, who is affiliated with the university’s ATLAS Institute, which prides itself on fostering out-of-the-box ideas.
Bruns started a company with tattoo-artist-to-the-stars Keith “Bang Bang” McCurdy, along with a former doctoral student. Early next year, they plan to release their first product, Magic Ink, to a group of handpicked artists. The business partners have long-term hopes for smart tattoos that have a health value, but cosmetics are cheaper and simpler to get to consumers than medical devices. So, that’s where they’re starting.
The new ink will enter a market in a moment of flux for the regulation of cosmetics. The FDA steps in to urge a recall if an ink causes a bacterial outbreak but traditionally has not exercised its regulatory might over tattoo ink products as it does with other products that go into the body. (Tattoo inks don’t even have to be sterile.) But following the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022, the FDA is expanding its authority over tattoo manufacturers. The agency is now accepting comments on draft guidance about tattoo ink preparation.
…
Read the full article here