Kate Wells, Michigan Radio | KFF Health News (TNS)
For more than 20 years, the National Eating Disorders Association has operated a phone line and online platform for people seeking help for anorexia, bulimia, and other eating disorders. Last year, nearly 70,000 individuals used the help line.
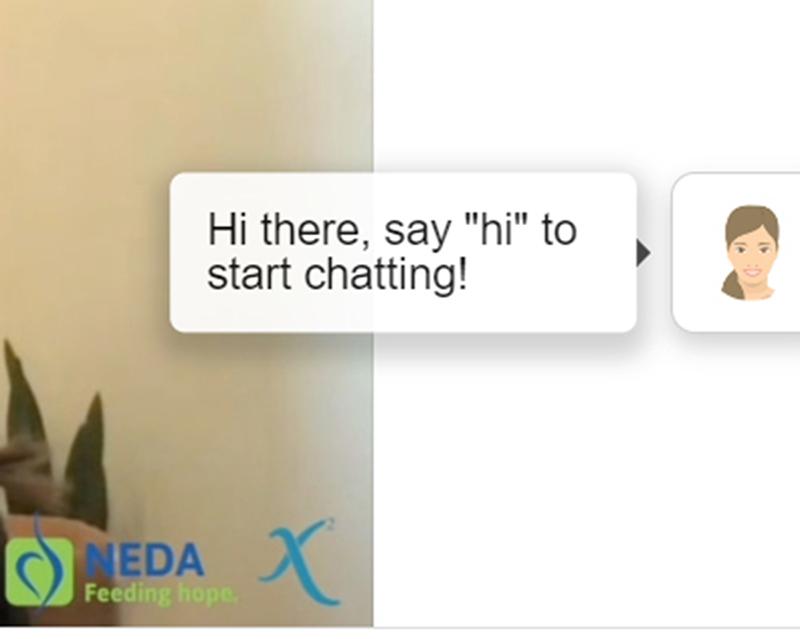
NEDA shuttered that service in May, saying that, in its place, a chatbot called Tessa, designed by eating disorder experts with funding from NEDA, would be deployed.
When NPR aired a report about this last month, Tessa was up and running online. Since then, both the chatbot’s page and a NEDA article about Tessa have been taken down. When asked why, NEDA said the bot is being “updated,” and the latest “version of the current program [will be] available soon.”
Then NEDA announced on May 30 that it was indefinitely disabling Tessa. Patients, families, doctors, and other experts on eating disorders were stunned. The episode has set off a fresh wave of debate as companies turn to artificial intelligence as a possible solution for a mental health crisis and treatment shortage.
Paid staffers and volunteers for the NEDA help line said that replacing the service with a chatbot could further isolate the thousands of people who use it when they feel they have nowhere else to turn.
“These young kids … don’t feel comfortable coming to their friends or their family or anybody about this,” said Katy Meta, a 20-year-old college student who has volunteered for the help line. “A lot of these individuals come on multiple times because they have no other outlet to talk with anybody. … That’s all they have, is the chat line.”
The decision is part of a larger trend: Many mental health organizations and companies are struggling to provide services and care in response to a sharp escalation in demand, and some are turning to chatbots and AI, even though clinicians are still trying to figure out how to effectively deploy them, and for what conditions.
The help…
Read the full article here